Celiac disease (mechanism of disease)
Вставка
- Опубліковано 2 кві 2023
- This is a mechanism of disease map for Celiac disease, which briefly covers the etiology, pathophysiology, and manifestations of Celiac disease.
ADDITIONAL TAGS:
Extraintestinal symptoms:
-Dermatitis herpetiformis
-Reduced fertility or infertility
-Endo: autoimmune thyroid, T1DM
Other autoimmune: autoimmune hepatitis, IBD, RA, sarcoid
Inflammation / cell damage
Signs / symptoms
Labs / tests / imaging results
Celiac disease
Core concepts
Social determinants of
health / risk factors
Food / nutrient absorption
Microbial pathogenesis
Biochemistry
Flow gradients
Genetics / regulation
Pain / neurology
Pathophysiology
Etiology
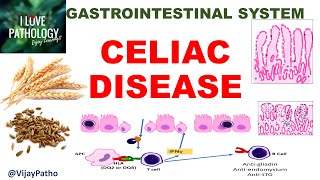
Immunological reaction to part of gluten
Consumption of food containing gluten
Release of tissue transglutaminase is triggered (enzyme from endothelial cells in response to inflammation / mechanical irritation)
Gliadin, an alcohol-soluble fraction of gluten, is modified
T cells are activated and react to modified gliaden
Trigger chronic intestinal inflammation
Epithelial damage including villous atrophy, crypt hyperplasia, loss of brush border
Impaired resorption of nutrients in small intestine
Manifestations
Malabsorption
IgA tissue trans- glutaminase (tTG) Ab
Chronic / recurrent diarrhea
Steatorrhea
Flatulence, abdominal pain, bloating
Decreased appetite
Weight loss
Fatigue
Vitamin def
Anemia
Iron def
Hypocalcemia
Osteoporosis
Fractures
Children: failure to thrive, growth failure, delayed puberty
Genetic predisposition
(HLA-DQ2 in 90-95%;
HLA-DQ8 in 5-10%)
Consumption of grains such as wheat, rye, barley
Peripheral neuropathy
Vitamin B def
Numb / tingle / burn of hands / feet








❤❤ Good one there
❤❤best