Liver Lipogenesis in the Fed State | Part 15 Carbohydrate Foundations | Macronutrients Lecture 61
Вставка
- Опубліковано 28 вер 2024
- After glycogen repletion, the liver builds fat through lipogenesis. The lipogenic fructose hypothesis suggests that high fructose intake may lead to fatty liver Subscribe to Nourishable at / nourishable
This video is part 15 of the Carbohydrate Foundations module within a lecture series on the nutrition science of macronutrients.
Carbohydrate Foundations Lecture playlist: • Playlist
Macronutrients Lecture playlist: • Macronutrients Lectures
Follow Nourishable on twitter, facebook and instagram to stay up to date on all things nutrition.
/ nourishable
nourishable.tv
/ nourishable
Lecture Development, Hosting & Post-Production by Lara Hyde, PhD
www.nourishable.tv
Video Production by Robbie Hyde
/ chedderchowder
Opening Motion Graphics by Jay Purugganan www.c9studio.c...
The information in this video is not intended or implied to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. All content, including text, graphics, images and information, contained on or available through this video is for general information purposes only.
References
Chapter 5 Carbohydrates in Wardlaw’s Perspectives in Nutrition, 2019 (Editors: Byrd-Bredbenner, Moe, Berning and Kelley, 11th edition)
Chapter 2 - Carbohydrates in Modern Nutrition in Health and Disease, 2014 (Editors: Ross, Caballero, Cousins, Tucker and Ziegler; 11 edition)
pubmed.ncbi.nl...
pubmed.ncbi.nl...
pubmed.ncbi.nl...
Images
Figures created with BioRender
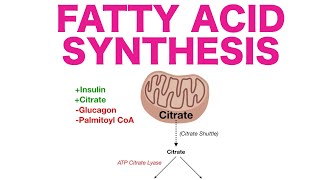
After hepatic glycogen has been repleted, the liver shuttles acetyl-CoA towards de novo lipogenesis. Insulin stimulates increased gene expression of genes that function as enzymes in lipogenesis, including acetyl-CoA carboxylase. Since fructose enters glycolysis later after the heavily regulated phosphofructokinase step, there is the potential for fructose to continue through glycolysis and yield acetylCoA even when the energy levels of the cell are high. This acetylCoA build up can then be shuttled towards de novo lipogenesis and may yield excessive lipid synthesis and storage in the liver. This is known as the lipogenic fructose hypothesis. High fructose feeding studies in animals support the development of fatty liver and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), however human studies are less conclusive.








Thanks for this little analysis. Finally something that goes further than the popular fear mongering "fructose bad" hysteria and puts things in perspective.