Це відео не доступне.
Перепрошуємо.
Electrocardiogram || ECG | ECG Wave | CVS Physiology
Вставка
- Опубліковано 17 жов 2022
- Electrocardiogram || ECG | ECG Wave | CVS Physiology
• Lecture content:
Electrocardiogram
Electrocardiography
The process of producing an electrocardiogram
Electrocardiogram
A recording of the electrical activity of the heart.
An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a test that checks how your heart is functioning by measuring the electrical activity of the heart. With each heartbeat, an electrical impulse (or wave) travels through your heart. This wave causes the muscle to squeeze and pump blood from the heart.
An ECG measures and records the electrical activity that passes through the heart. A doctor can determine if this electrical activity is normal or irregular.
An ECG may be recommended if you are experiencing arrhythmia, chest pain, or palpitations and an abnormal ECG result can be a signal of a number of different heart conditions.
What can you expect?
• An ECG is a non-invasive procedure, which means that nothing is injected into the body.
• It is painless.
• A number of electrodes - usually a total of 12 to 15 - are attached to various locations on your body including your arm, leg and chest.
• The electrodes are attached by small suction cups or adhesive patches.
• Sensors in the pads detect the electrical activity of your heart.
• The test is usually performed while you lie still.
• Results are most often recorded on graph paper and interpreted or read by your doctor or a technologist.
• The test usually takes 5 to 10 minutes.
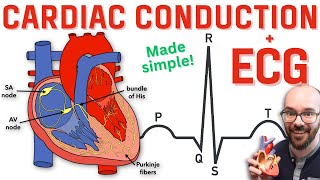
P, Q, R, S, T Waves:
P Wave
The electrical activity of the heart originates in the sino-atrial node. The impulse then rapidly spreads through the right atrium to the atrioventricular node. It also spreads through the atrial muscle directly from the right atrium to the left atrium. The P-wave is generated by activation of the muscle of both atria.
Q, R, S Wave
The impulse travels very slowly through the AV node, then very quickly through the bundle of His, then the bundle branches, the Purkinje network, and finally the ventricular muscle.
The first area of the ventricular muscle to be activated is the interventricular septum, which activates from left to right. This generates the Q-wave.
Next, the left and right ventricular free walls, which form the bulk of the muscle of both ventricles, gets activated, with the endocardial surface being activated before the epicardial surface. This generates the R-wave.
A few small areas of the ventricles are activated at a rather late stage. This generates the S-wave.
Finally, the ventricular muscle repolarizes. This generates the T-wave.
To understand the morphology of the ECG waveforms one needs to appreciate only one biophysical fact: if a wave front of depolarization travels towards the electrode attached to the + input terminal of the ECG amplifier and away from the electrode attached to the - terminal, a positive-going deflection will result. If the waveform travels away from the + electrode towards the - electrode, a negative going deflection will be seen.
I hope u will enjoy the whole lecture if it is helpful plz like share and subscribe✌✔ .
physiology || biochemistry and anatomy ||cardiovascular system physiology || CVS physiology || cardiovascular system physiology in hindi || mbbs physiology lecturers || mbbs 1st year lecturers || mbbs lecturers || mbbs biochemistry lecturers || chill medicos || NEXT ||neetpg || neet
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
CHAPTERS
00:05-- Introduction
00:44-- Introduction of electrocardiogram
01:43-- Uses of ECG
02:33-- ECG Leads
10:22-- Waves of normal ECG
11:42-- Electrocardiographic grid
16:05 --- Interval of normal ECG
19:08--- Clinical significance of ECG waves
24:23-- Clinical significance of interval and segments
_______________________________________________
• Links :
• For queries join my public telegram group : t.me/Chillmedico
• For notes join official telegram channel : t.me/Chillmedicos14
• Facebook page : / himanshudaso. .
• Instagram page : / chill.medico
• You tube channel : / chillmedicos140
~ Chill medicos provides University based important lecturers and notes..
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
• Mentions :
@Chill Medicos @Biochemistry by Dr Rajesh Jambhulkar @Physiology by Doctor Nagi @Institute of Human Anatomy
___________________~~~~~~~~____________
#electrocardiogram #ecg #ecgwaves #CVS #cardiovascularsystem #cardiovascularsystemphysiology #physiology #physiologylectures #mbbs1styear #anatomyandphysiology #NEXT #neetpg #neet #mbbs #chillmedicos








Jazakallah hu khair sir..(Thank you so much sir
Dhanyawaad sir
Thik hai × 1000
😂
Thik hai, Thik hai 😊
Sir thanks for making basics more clear
Tqsm sir 🙏🙏... Much needed channel.. glad to find ur channel ❤️❤️
Tnq 😊
Thank you so much sir 😊
Much needed channel
Tnq ❤️
THANKYOU SO MUCH YOU ARE JUST A GREAT ✅
Tysm sir wonderfull lectures 😊
TQ 🥰